USA Independence Day, July 4, 2007
 |
Washington DC; On July 4, 1776, our Nation's Founders declared "That these United Colonies are, and of Right, ought to be free and Independent States." This declaration marked a great milestone in the history of human freedom. On the 230th anniversary of the signing of the Declaration of Independence, we pay tribute to the courage and dedication of those who created this country, and we celebrate the values of liberty and equality that make our country strong.
The patriots of the Revolutionary War acted on the beliefs that "all men are created equal" and "that they are endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable Rights." By advancing these ideals, generations of Americans have unleashed the hope of freedom for people in every corner of the world.
As we celebrate our independence, Americans can take pride in our history and look to the future with confidence. We offer our gratitude to all the American patriots, past and present, who have sought to advance freedom and lay the foundations of peace. Because of their sacrifice, this country remains a beacon of hope for all who dream of liberty and a shining example to the world of what a free people can achieve. May God continue to bless the United States of America.
NOW, THEREFORE, I, GEORGE W. BUSH, President of the United States of America, by virtue of the authority vested in me by the Constitution and laws of the United States, do hereby proclaim July 4, 2006, as Independence Day. I call upon the people of the United States to observe with all due ceremony our Independence Day as a time to honor our Founders and their legacy of freedom and remember with thankfulness the sacrifice of our men and women in uniform.
IN WITNESS WHEREOF, I have hereunto set my hand this twenty-sixth day of June, in the year of our Lord two thousand six, and of the Independence of the United States of America the two hundred and thirtieth.
GEORGE W. BUSH
President of The United States of America
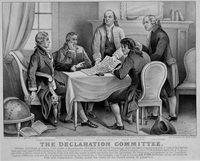 Lithograph. The Declaration Committee. By Currier and Ives. New York, 1876. Prints and Photographs Division (8) LC-USZ62-820 (b&w) |
Declaring Our Independence
Chronology Of Events: June 7, 1776 to January 18, 1777 1776 June 7 -- Congress, meeting in Philadelphia, receives Richard Henry Lee's resolution urging Congress to declare independence.
June 11 -- Thomas Jefferson, John Adams, Benjamin Franklin, Roger Sherman, and Robert R. Livingston appointed to a committee to draft a declaration of independence. American army retreats to Lake Champlain from Canada.
June 12 - 27 -- Jefferson, at the request of the committee, drafts a declaration, of which only a fragment exists. Jefferson's clean, or "fair" copy, the "original Rough draught," is reviewed by the committee. Both documents are in the manuscript collections of the Library of Congress.
June 28 -- A fair copy of the committee draft of the Declaration of Independence is read in Congress.
July 1 - 4 -- Congress debates and revises the Declaration of Independence.
July 2 -- Congress declares independence as the British fleet and army arrive at New York.
July 4 -- Congress adopts the Declaration of Independence in the morning of a bright, sunny, but cool Philadelphia day. John Dunlap prints the Declaration of Independence. These prints are now called "Dunlap Broadsides." Twenty-four copies are known to exist, two of which are in the Library of Congress. One of these was Washington's personal copy.
July 5 -- John Hancock, president of the Continental Congress, dispatches the first of Dunlap's broadsides of the Declaration of Independence to the legislatures of New Jersey and Delaware.
July 6 -- Pennsylvania Evening Post of July 6 prints the first newspaper rendition of the Declaration of Independence.
July 8 -- The first public reading of the Declaration is in Philadelphia.
July 9 -- Washington orders that the Declaration of Independence be read before the American army in New York -- from his personal copy of the "Dunlap Broadside."
July 19 -- Congress orders the Declaration of Independence engrossed (officially inscribed) and signed by members.
August 2 -- Delegates begin to sign engrossed copy of the Declaration of Independence. A large British reinforcement arrives at New York after being repelled at Charleston, S.C.
1777 January 18 -- Congress, now sitting in Baltimore, Maryland, orders that signed copies of the Declaration of Independence printed by Mary Katherine Goddard of Baltimore be sent to the states.
Drafting the Documents
Thomas Jefferson drafted the Declaration of Independence in Philadelphia behind a veil of Congressionally imposed secrecy in June 1776 for a country wracked by military and political uncertainties. In anticipation of a vote for independence, the Continental Congress on June 11 appointed Thomas Jefferson, John Adams, Benjamin Franklin, Roger Sherman, and Robert R. Livingston as a committee to draft a declaration of independence. The committee then delegated Thomas Jefferson to undertake the task. Jefferson worked diligently in private for days to compose a document. Proof of the arduous nature of the work can be seen in the fragment of the first known composition draft of the declaration, which is on public display here for the first time.
Jefferson then made a clean or "fair" copy of the composition declaration, which became the foundation of the document, labeled by Jefferson as the "original Rough draught." Revised first by Adams, then by Franklin, and then by the full committee, a total of forty-seven alterations including the insertion of three complete paragraphs was made on the text before it was presented to Congress on June 28. After voting for independence on July 2, the Congress then continued to refine the document, making thirty-nine additional revisions to the committee draft before its final adoption on the morning of July 4. The "original Rough draught" embodies the multiplicity of corrections, additions and deletions that were made at each step. Although most of the alterations are in Jefferson's handwriting (Jefferson later indicated the changes he believed to have been made by Adams and Franklin), quite naturally he opposed many of the changes made to his document.
Congress then ordered the Declaration of Independence printed and late on July 4, John Dunlap, a Philadelphia printer, produced the first printed text of the Declaration of Independence, now known as the "Dunlap Broadside." The next day John Hancock, the president of the Continental Congress, began dispatching copies of the Declaration to America's political and military leaders. On July 9, George Washington ordered that his personal copy of the "Dunlap Broadside," sent to him by John Hancock on July 6, be read to the assembled American army at New York. In 1783 at the war's end, General Washington brought his copy of the broadside home to Mount Vernon. This remarkable document, which has come down to us only partially intact, is accompanied in this exhibit by a complete "Dunlap Broadside" -- one of only twenty-four known to exist.
On July 19, Congress ordered the production of an engrossed (officially inscribed) copy of the Declaration of Independence, which attending members of the Continental Congress, including some who had not voted for its adoption, began to sign on August 2, 1776. This document is on permanent display at the National Archives.
On July 4, 1995, more than two centuries after its composition, the Declaration of Independence, just as Jefferson predicted on its fiftieth anniversary in his letter to Roger C. Weightman, towers aloft as "the signal of arousing men to burst the chains...to assume the blessings and security of self-government" and to restore "the free right to the unbounded exercise of reason and freedom of opinion."
The Declaration of Independence Documents in Library of Congress



